Google and Mozilla decide to ban Chinese certificate authority CNNIC from Chrome and Firefox
Google and Mozilla have announced that their browsers will stop trusting all digital certificates issued by the China Internet Network Information Center (CNNIC), China’s main digital certificate authority. The decision follows last week’s news from Google, which said on March 20 it discovered unauthorized digital certificates for several of its domains. Google found that the certificates were issued by Egypt-based MCS Holdings, an intermediate certificate authority that CNNIC allowed to operate.
On April 1, Google updated its blog post with the following statement:
As a result of a joint investigation of the events surrounding this incident by Google and CNNIC, we have decided that the CNNIC Root and EV CAs will no longer be recognized in Google products. This will take effect in a future Chrome update. To assist customers affected by this decision, for a limited time we will allow CNNIC’s existing certificates to continue to be marked as trusted in Chrome, through the use of a publicly disclosed whitelist.
While neither we nor CNNIC believe any further unauthorized digital certificates have been issued, nor do we believe the misissued certificates were used outside the limited scope of MCS Holdings’ test network, CNNIC will be working to prevent any future incidents. CNNIC will implement Certificate Transparency for all of their certificates prior to any request for reinclusion. We applaud CNNIC on their proactive steps, and welcome them to reapply once suitable technical and procedural controls are in place.
In other words, Chrome users will get security warnings for new sites authenticated by CNNIC, particularly those that require entering login information. Some pages, such as those involving monetary transactions, will simply stop working (any bank or commerce site worth its salt will not allow money to move without proper security).
Google does not say when exactly this change will go into effect (the company typically specifies a Chrome version number for security changes and updates). It likely wants to give affected website operators time to switch to a different certificate authority.
CNNIC responded on April 2 (today) with the following:
1. The decision that Google has made is unacceptable and unintelligible to CNNIC, and meanwhile CNNIC sincerely urge that Google would take users’ rights and interests into full consideration.
2. For the users that CNNIC has already issued the certificates to, we guarantee that your lawful rights and interests will not be affected.
It’s not clear whether CNNIC plans to do something specific in regards to the second point. The firm is likely still weighing its options.
Mozilla followed in Google’s footsteps today:
After reviewing the circumstances and a robust discussion on our public mailing list, we have concluded that CNNIC’s behaviour in issuing an unconstrained intermediate certificate to a company with no documented PKI practices and with no oversight of how the private key was stored or controlled was an ‘egregious practice’ as per Mozilla’s CA Certificate Enforcement Policy. Therefore, after public discussion and consideration of the scope and impact of a range of options, we have decided to update our code so that Mozilla products will no longer trust any certificate issued by CNNIC’s roots with a notBefore date on or after 1st April 2015.
The notBefore date that will be checked is inserted into the certificate by CNNIC. We will therefore be asking CNNIC for a comprehensive list of their currently-valid certificates, and publishing it. After the list has been provided, if a certificate not on the list, with a notBefore date before 1 April 2015, is detected on the public Internet by us or anyone else, we reserve the right to take further action.
Like Google, Mozilla is offering CNNIC the option to reapply for full inclusion. The restriction thus might be removed assuming CNNIC meets Google’s and Mozilla’s requirements.
If Chrome and Firefox were to stop recognizing all website certificates issued by CNNIC, the impact could be huge in China; millions of users would suddenly not be able to connect to various websites. Presumably, Google and Mozilla will wait a reasonable amount of time before flipping the switch, so website operators can ensure their sites will continue to work as expected.

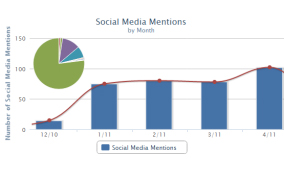
 Article spinning, keyword stuffing, excessive bookmarks, paid links, thin content, duplicate content, excessive blog commenting, etc. were once widely regarded as acceptable SEO tactics. Now those tactics can land you in big trouble with Google. Thanks to Google Panda and Penguin, nothing about SEO is quick, easy or cheap.
Article spinning, keyword stuffing, excessive bookmarks, paid links, thin content, duplicate content, excessive blog commenting, etc. were once widely regarded as acceptable SEO tactics. Now those tactics can land you in big trouble with Google. Thanks to Google Panda and Penguin, nothing about SEO is quick, easy or cheap. After its IPO missteps, Facebook went all out to raise revenue with numerous advertising products. Though plenty of money has been made, particularly with mobile advertising, Facebook plans to simplify its advertising product based on feedback from marketers. The launch of Facebook video ads, scheduled for Fall 2013, is on hold due to concerns about user experience. At an estimated $1 million to $2.4 million per daily spot, we think it’s safe to say that Facebook will figure it out and start rolling those video ads before too long.
After its IPO missteps, Facebook went all out to raise revenue with numerous advertising products. Though plenty of money has been made, particularly with mobile advertising, Facebook plans to simplify its advertising product based on feedback from marketers. The launch of Facebook video ads, scheduled for Fall 2013, is on hold due to concerns about user experience. At an estimated $1 million to $2.4 million per daily spot, we think it’s safe to say that Facebook will figure it out and start rolling those video ads before too long.
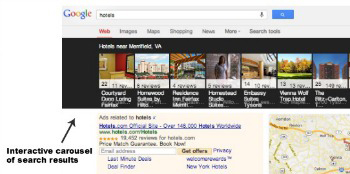
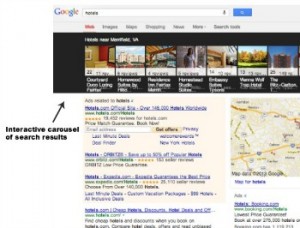 Recently, Google introduced Carousel for local search results. Now, when you search for a local business like a hotel or restaurant, the results appear in an interactive carousel at the top of the page. Click on one of the results in the carousel and you’ll see the address, photos, overall review-based score and links to the actual reviews.
Recently, Google introduced Carousel for local search results. Now, when you search for a local business like a hotel or restaurant, the results appear in an interactive carousel at the top of the page. Click on one of the results in the carousel and you’ll see the address, photos, overall review-based score and links to the actual reviews.
 *According to the most recent internet usage data published in June 2012 by Nielsen Online and reported by
*According to the most recent internet usage data published in June 2012 by Nielsen Online and reported by 
Recent Comments